Receiving a borderline Electrocardiogram (ECG) result can be unsettling, leaving patients and healthcare providers seeking clarity. This guide provides a detailed diagnostic approach, explaining ECG complexities in an accessible manner to empower informed decisions about cardiovascular health. For more in-depth information, see this helpful guide: Borderline ECG Explained.
Decoding Borderline ECGs: Heart Sounds and Diagnostic Steps
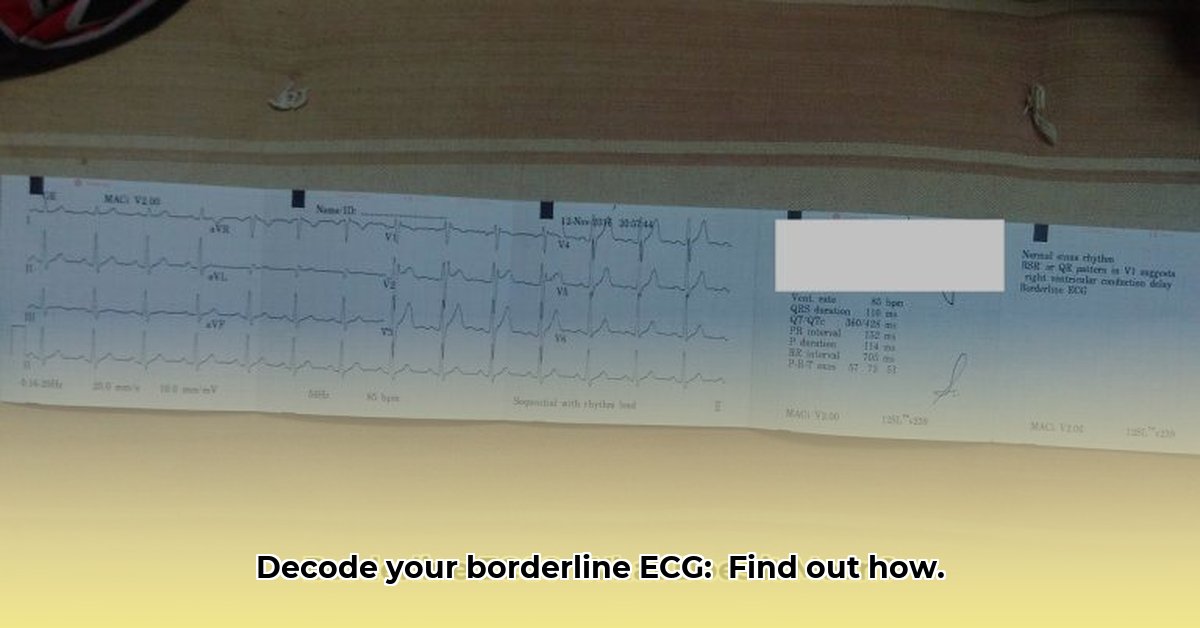
A borderline ECG signifies that the heart’s electrical activity is neither clearly normal nor abnormal, demanding further investigation. While it’s not immediately alarming, it necessitates a comprehensive evaluation. Studies indicate that these findings occur in approximately 20% of routine ECG screenings.
Cardiovascular Diagnosis: A Collaborative Approach
Interpreting a borderline ECG involves careful consideration of multiple factors:
- Personal History: Lifestyle elements, including exercise habits, diet, stress levels, smoking status, and medications, significantly impact ECG results.
- Cardiac Testing: An ECG provides a snapshot. Additional tests, such as stress tests, echocardiograms, or Holter monitors, offer more comprehensive data.
- Expert Interpretation: Cardiologists specializing in electrophysiology possess the expertise to identify subtle ECG patterns. Seek consultation with a qualified specialist for accurate diagnosis.
Overcoming Diagnostic Hurdles in Heart Disease
A major challenge in diagnosing borderline ECGs is the absence of a universally accepted definition of “borderline.” This ambiguity, coupled with uncertainty regarding potential serious heart conditions, emphasizes the need to assess all facets of a patient’s health, including previous medical history and existing conditions.
Actionable Steps for Patients and Healthcare Providers in Cardiac Care
For Patients:
- Consult a Cardiologist: Discuss your results and address any questions or concerns. Seek clarification on ambiguous findings.
- Adhere to Diagnostic Recommendations: Undergo recommended tests to obtain a complete understanding of your heart health.
- Adopt a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle: Incorporate a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques. Refrain from smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
For Healthcare Providers:
- Gather Patient History: Obtain a thorough patient history, including lifestyle factors, stress levels, family history of heart disease, and current medications.
- Tailor ECG Testing: Select appropriate additional tests based on borderline ECG findings and individual patient characteristics.
- Communicate Clearly: Explain results to patients in an understandable manner, emphasizing the need for further evaluation.
- Maintain Detailed Records: Document all findings, investigations, and management plans for longitudinal tracking of patient progress.
The Future of ECG Analysis: Merging Technology and Expertise
Advanced technologies, such as AI-assisted ECG interpretation systems, are being developed to enhance diagnostic accuracy. However, these tools are designed to support, not replace, the expertise of experienced cardiologists.
Technology’s Impact on Heart Monitoring: Weighing Benefits and Limitations
| Technology | Potential Advantages | Potential Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| AI-assisted ECG Interpretation | Accelerated analysis, improved diagnostic accuracy potential | Algorithmic bias potential, dependence on data integrity |
| Traditional ECG Interpretation | Proven methodology, leveraging human expertise | Time-intensive, susceptible to human error in interpretation |
Borderline ECG results necessitate thorough investigation, integrating scientific precision, clinical judgment, and comprehensive patient history for accurate diagnoses.
Interpreting Borderline ECG Results: A Guide to Next Steps
Key Takeaways:
- A borderline ECG is not a definitive diagnosis but a prompt for further evaluation.
- Various factors, including stress, electrolyte imbalances, and underlying health conditions, can cause borderline ECG results.
- Effective interpretation involves collaboration between patients and healthcare providers.
- Further testing is critical to determine the underlying cause of abnormal readings.
- Maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle is essential for overall cardiovascular well-being.
Deciphering the ECG Puzzle: The Meaning of “Borderline”
An ECG records the heart’s electrical activity. A “borderline” result suggests slight deviations from the norm, necessitating attention.
Common Causes of Borderline ECG Results
Borderline ECGs occur in approximately 20% of cases. Possible causes include:
- Stress and Anxiety: These can manifest as rhythm variations on an ECG.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Fluctuations in potassium, sodium, calcium, or magnesium levels affect heart rhythm.
- Medications: Certain medications can alter ECG patterns.
- Technical Factors: Improper lead placement or equipment malfunction can lead to inaccurate results.
Patient Guide: Interpreting Borderline ECG Results and Next Steps
- Remain Calm: A borderline result does not confirm a diagnosis.
- Schedule a Consultation: Discuss your results with your healthcare provider to evaluate your individual risk factors.
- Provide Context: Inform your doctor about any symptoms (chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath).
- Adopt Heart-Healthy Habits: Your doctor may recommend lifestyle modifications, such as stress reduction techniques, a balanced diet, and regular exercise.
- Pursue Further Testing: Your doctor may order additional tests, including repeat ECGs, Holter monitoring, stress tests, or echocardiograms.
Physician’s Perspective: Interpreting Borderline ECG Results
Healthcare professionals interpreting borderline ECGs must carefully consider patient history, symptoms, medications, and lifestyle factors. Next steps may involve:
- Thorough Review: Review the ECG tracing and patient’s medical history.
- Risk Stratification: Assess the patient’s individual risk profile for cardiovascular disease.
- Targeted Testing: Order appropriate tests based on risk stratification.
- Patient Education: Clearly explain results and recommendations to alleviate anxiety.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Schedule regular follow-up ECGs or other monitoring as needed.
Addressing the Uncertainties
Variations exist in the management of borderline ECGs, particularly in asymptomatic individuals. Comparing the effectiveness of different follow-up tests (e.g., stress tests vs. Holter monitors) is important for guiding clinicians and improving patient outcomes.
Managing Borderline ECG Results in Older Adults With Cardiac Conditions
Key Takeaways:
- Borderline ECGs are common, ambiguous findings requiring careful interpretation.
- A comprehensive approach integrates ECG results with clinical data.
- Further testing may be necessary for accurate diagnosis and risk assessment.
- Management decisions depend on individual patient factors and risk profiles.
- Managing borderline ECG results in geriatric patients requires a nuanced, personalized strategy.
Challenges in Diagnosing Borderline ECGs in Older Patients
Age-related changes in the heart can mimic disease, complicating the interpretation of electrocardiograms (ECGs), especially borderline ECGs.
Individualized Care for Borderline Cases in Geriatric Cardiac Patients
When managing borderline ECG results in geriatric patients, consider the patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and symptoms, given the increased prevalence of comorbidities.
Diagnostic Strategies: When to Investigate Further
Consider these situations as indications for further investigation:
- Persistent or worsening symptoms: Chest pains, shortness of breath, or dizziness.
- Significant risk factors: History of heart disease, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, or smoking.
- ECG changes suggestive of potential issues: Subtle abnormalities that raise suspicion of cardiac ischemia or arrhythmias.
Diagnostic Tests for Clarification
Non-invasive tests providing a comprehensive view of heart health include:
- Holter Monitor: Detects intermittent arrhythmias over 24-48 hours.
- Stress Test: Evaluates the heart’s response to exercise, helping identify ischemia.
- Echocardiogram: Provides detailed images of the heart, assessing its structure and function.
Managing Results and Moving Forward
Management plans integrating all test findings should reflect an overall assessment involving collaboration among the patient, their primary care physician, and a cardiologist. Open communication and shared decision-making are key.
- Transcendental Meditation Books Guiding Your Journey to Deeper Practice - March 3, 2026
- Your TM Meditation Book Explores Its Benefits and History - March 2, 2026
- Daily Mindfulness Readings Cultivate Inner Peace and Presence Every Day - March 1, 2026