Chest pain and a confusing ECG result can be worrying, leaving you unsure of the next steps. This guide explains what a borderline ECG means, potential causes, and crucial steps to take, providing clarity and confidence. Whether you’re a patient or a healthcare professional, this information will help you move forward effectively.
Borderline ECG: Interpretation and Immediate Actions
Experiencing chest pain coupled with a “borderline” ECG result? It’s understandable to feel concerned. Let’s simplify this and outline the necessary next steps. A borderline ECG suggests slight abnormalities, but doesn’t definitively point to a major issue. This “fuzzy picture” warrants further investigation to gain clarity about your heart health using sophisticated technology.
Decoding That Borderline ECG for Accurate Heart Monitoring
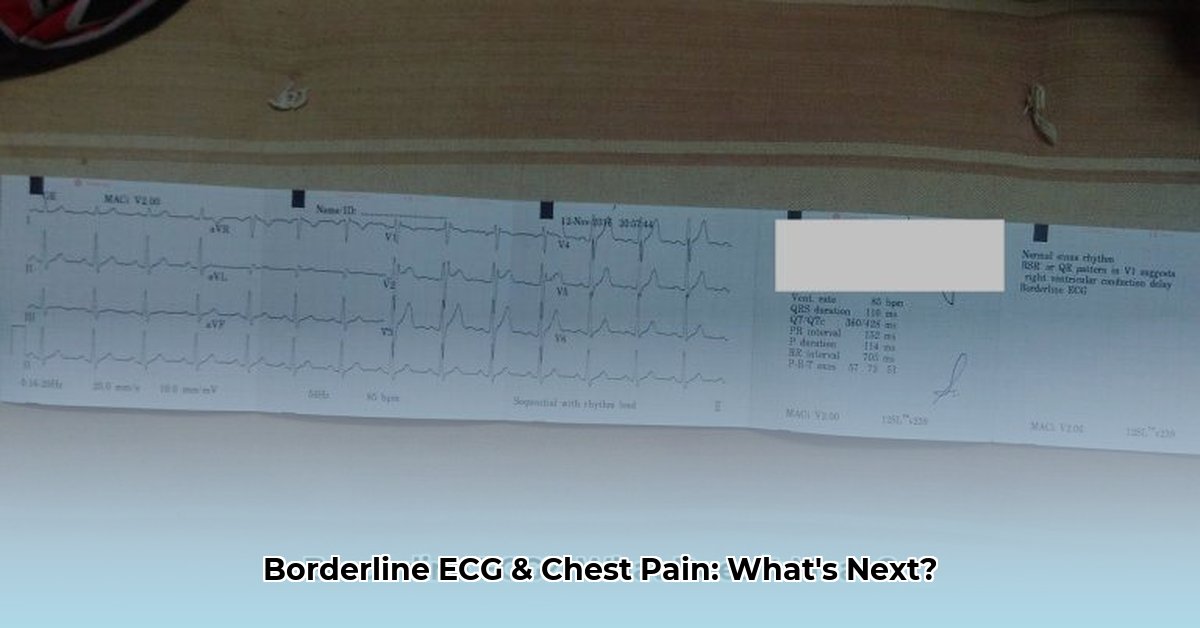
An electrocardiogram (ECG) records your heart’s electrical activity. A borderline ECG indicates slight anomalies, not a clear diagnosis. Several factors can influence ECG readings, including age, health history, and electrode placement. Chest pain alongside a borderline ECG requires immediate attention. It’s crucial to understand that a borderline ECG is not a definitive diagnosis but rather a sign that further investigation is warranted. The ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart, and deviations from the norm, even slight ones, need to be carefully evaluated. These deviations can be caused by a variety of factors, some benign, others potentially serious.
Your Next Steps: Comprehensive Cardiac Assessment
A thorough checkup is crucial. Your doctor will consider your health history alongside the ECG reading. This involves a detailed review of your medical history, a thorough physical examination, and a careful consideration of your symptoms.
- Schedule a Follow-Up: Discuss symptoms and ECG results with your doctor promptly to get answers. Don’t delay, as timely diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
- Further Diagnostic Testing: Your doctor might suggest further evaluations like a repeat ECG, echocardiogram, stress test, or Holter monitor. Additional tests will help paint a clearer picture. The specific tests recommended will depend on your individual circumstances and risk factors.
- Echocardiogram: Assesses heart structure and pumping efficiency with high accuracy. This non-invasive test provides detailed images of the heart’s valves, chambers, and overall function.
- Stress Test: Evaluates how your heart functions under physical stress, often involving walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike while your heart’s electrical activity is monitored.
- Holter Monitor: A portable device that continuously records your heart’s rhythm over a period of 24 to 48 hours, helping to detect intermittent arrhythmias.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regardless of the ECG results, adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet. This includes quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Open Communication: Share your concerns and describe symptoms accurately with your doctor. Active involvement is essential for effective care. Ask questions and ensure you understand the reasons for any recommended tests or treatments.
Testing Time: Weighing the Pros and Cons for Informed Decisions
Your physician might recommend tests, each with benefits and drawbacks:
| Test | Advantages | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Repeat ECG | Quick, easy, inexpensive; confirms initial findings’ consistency. | Limited detailed information about heart structure. |
| Echocardiogram | Detailed images of heart structure and function. | Requires prep work; may cause mild anxiety for some patients. |
| Stress Test | Assesses heart function under stress; can identify ischemia. | Potential risks for high-risk individuals; may require medication adjustments. |
| Holter Monitor | Continuous heart rhythm tracking over extended periods; detects intermittent arrhythmias. | Possible skin irritation; requires careful adherence to instructions; can be inconvenient to wear. |
| Cardiac CT Scan | Provides detailed images of the coronary arteries; can detect blockages. | Exposure to radiation; may require contrast dye, which can cause allergic reactions. |
Managing Uncertainty and Next Steps for Borderline ECG
Uncertainty about health issues can be unsettling. Remember that addressing medical questions takes time. Focus on what you can control: adopting a healthy lifestyle, attending your appointments, and communicating openly with your healthcare provider.
Understanding Borderline ECG and Chest Pain Management
Key Takeaways:
- A borderline ECG necessitates additional tests, as it doesn’t provide enough detail.
- Chest pain with a borderline ECG requires prompt actions to determine underlying issues.
- Interpreting the ECG involves analyzing symptoms and assessing medical history for comprehensive insights.
- Further investigations can bring greater clarity and deeper insights.
What Does a Borderline ECG Mean for Your Heart Health?
Think of an electrocardiogram (ECG) is like a recording of your heart’s activity. A borderline ECG suggests the recording is a little unclear, indicating possible irregularities but not definitively showing a problem. It’s neither completely normal nor clearly abnormal. This ambiguity is why how to interpret borderline ecg results and determine next steps is a crucial question. It requires a more detailed investigation. Consider it a yellow flag prompting further scrutiny.
This uncertainty is often due to factors like stress, dehydration, medication side effects, or even minor technical issues during the ECG recording. Sometimes, it simply reflects normal variations in heart rhythm. However, it could also indicate underlying cardiac issues needing prompt attention. Therefore, dismissing a borderline result is not wise. Potential underlying conditions can range from electrolyte imbalances to early signs of coronary artery disease.
Chest Pain and Borderline ECG: When Is a Cardiac Evaluation Needed?
Chest pain alongside a borderline ECG raises the stakes. Chest pain can stem from various sources, including heart problems or anxiety. The combination of pain and an unclear ECG necessitates a thorough evaluation. Don’t hesitate to seek immediate medical attention if you experience persistent or severe chest pain, especially if accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or dizziness. These symptoms could indicate a serious cardiac event, such as a heart attack or unstable angina.
How to Interpret Borderline ECG Results and Determine Next Steps: A Systematic Approach
What’s the next step if you receive a borderline ECG? Working with your physician is essential. They’ll consider various factors:
- Your Symptoms: Your doctor meticulously reviews your symptoms. The nature, duration, and severity of your chest pain, if any, is key. Other symptoms, like shortness of breath or palpitations, are also evaluated. Be prepared to describe your symptoms in detail, including when they started, what makes them better or worse, and any other relevant information.
- Medical History: Your personal and family medical history helps them assess risk. Do you have hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, or a family history of heart disease? These factors influence the interpretation.
- Physical Exam: A comprehensive physical exam assesses your overall health. Your blood pressure, heart rate, and lung sounds are checked. The doctor will also look for any signs of underlying conditions that could be contributing to your symptoms.
- Further Testing: Based on the initial evaluation, your doctor may order additional tests:
- Repeat ECG: A simple repeat ECG can sometimes clarify inconsistencies. It is important to ensure that the ECG is performed under consistent conditions (e.g., same time of day, same level of activity).
- Stress Test: This test assesses your heart’s function under exertion, revealing potential problems that might not appear during rest. There are several types of stress tests, including exercise stress tests and pharmacological stress tests.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of your heart provides detailed images of its structure and function. This can help identify valve problems, heart muscle abnormalities, and other structural issues.
- Holter Monitor: A portable ECG worn for 24-48 hours records your heart rhythm continuously, detecting intermittent irregularities. This is particularly useful for detecting arrhythmias that may not be present during a standard ECG.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can rule out underlying conditions influencing the ECG, such as electrolyte imbalances, thyroid disorders, or anemia. They can also measure cardiac enzymes, which can indicate heart damage.
Making Sense of the Results of an Electrocardiogram
The additional tests provide a more complete picture. Based on these results, your doctor can determine if further intervention is needed. This might involve lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, stress management), medication, or even more advanced procedures, such as angioplasty or bypass surgery.
Interpreting Borderline ECGs in Patients with Chest Pain
Key Takeaways:
- A borderline ECG serves as a signal for further investigations, guiding the decisions ahead.
- Chest pain combined with a borderline ECG demands a comprehensive approach—a careful evaluation that guides medical decisions.
- Your medical history, symptoms, and ECG results are critical for assessments, leading the way for deeper insights into cardiovascular well-being.
- Stress tests, echocardiograms, and advanced tools are vital to gain clarity on the heart’s real-time functioning and structure.
What Does a Borderline ECG Mean for Cardiac Patients?
Imagine an ECG as detailed snapshots of your heart’s electrical activity. A “borderline” result means the reading falls into a gray area—neither clearly normal nor definitively abnormal. This ambiguity is why interpreting borderline ECGs in patients with chest pain presents a diagnostic challenge. It’s not a cause for immediate panic, but it does necessitate further exploration. It necessitates a thorough, nuanced analysis that considers the patient’s entire clinical picture.
Why the Uncertainty: Factors Affecting ECG Interpretations
- Best Books on Meditation Recommended by Mindfulness Experts - January 30, 2026
- Best Mindfulness Books for Anxiety, Sleep, and Daily Peace - January 29, 2026
- Books On Mindfulness For A Happier, More Present Life - January 28, 2026