Dizzy spells after a heart test? Don’t panic. A “borderline” ECG isn’t a diagnosis itself, but it means your doctor wants to take a closer look. This guide explains what a borderline ECG is in simple terms, connects it to dizziness, and helps you understand what steps to take next. We’ll cover potential causes, when to see a doctor right away, and what tests might be needed. Plus, we’ll share practical tips for a healthier heart and managing both your ECG results and that dizzy feeling. Let’s get you informed and feeling empowered.
Borderline ECG and Dizziness: Understanding Your Heart Rhythm
Feeling dizzy and getting a “borderline” result on your electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)? It’s understandable to feel a bit concerned. Let’s break it down in a way that’s easy to understand, focusing on heart rhythm and potential irregularities.
What’s a Borderline ECG, Anyway? Identifying Heart Irregularities
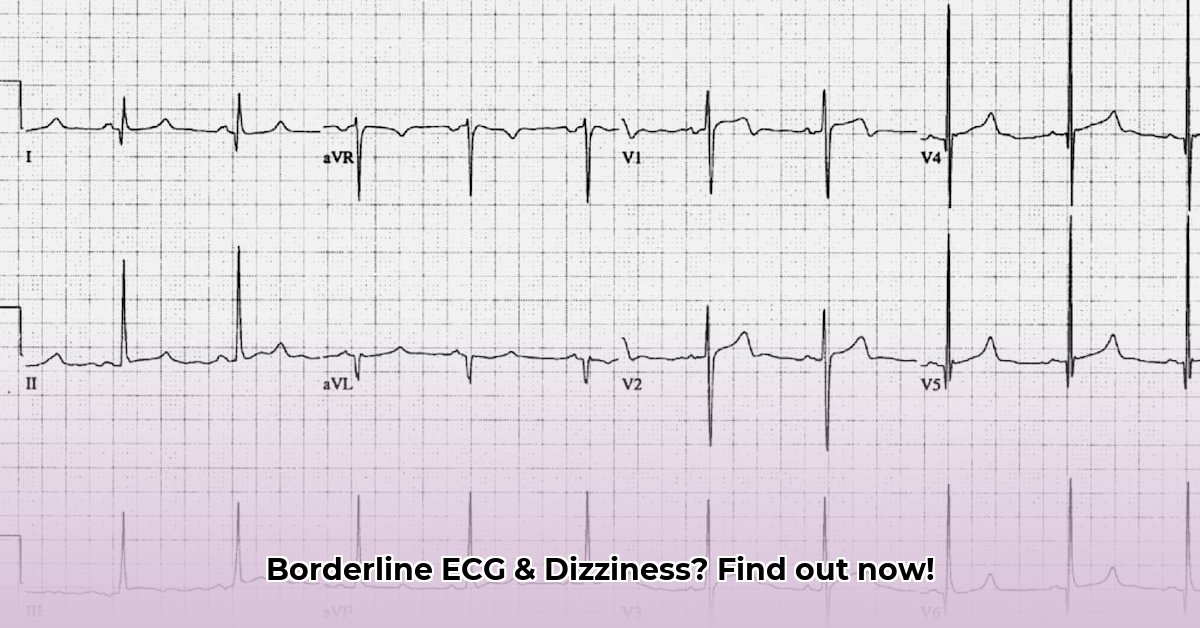
Think of your ECG as a snapshot of your heart’s electrical activity. It shows how your heart beats. A “borderline” ECG isn’t a diagnosis itself; it means some readings are slightly outside the perfectly normal range, but not enough to raise immediate alarm bells. It’s like finding a slightly smudged fingerprint at a crime scene – it’s interesting, and it warrants further investigation, but it doesn’t solve the case on its own. This often happens with specific measurements like the QT interval (the time it takes your heart to recharge between beats), the ST segment (a portion of the ECG that shows the heart’s electrical recovery), or the T wave (which reflects the repolarization of the heart). The dizziness adds another piece to the puzzle.
Why the Dizziness? Unraveling the Possible Causes of Lightheadedness
There are many reasons why you might experience dizziness alongside a borderline ECG. Sometimes it’s a simple issue that’s easily resolved. Other times, it might point to something needing further review by your healthcare provider. Let’s explore some possibilities:
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Electrolytes, like potassium and magnesium, are crucial minerals that regulate your heartbeat. An imbalance, perhaps due to dehydration or poor diet, can disrupt your heart rhythm and cause dizziness.
- Anxiety and Stress: Believe it or not, stress and anxiety can really impact your heart. They can make your heart beat faster and irregularly, leading to both dizziness and a borderline ECG reading. Think of it as your body’s natural alarm system getting a little overzealous.
- Minor Rhythm Variations: Slight irregularities in your heartbeat are pretty common. These subtle variations might show up as a borderline ECG result without causing any significant problems.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain medications, even common ones, can influence your heart rhythm and possibly cause dizziness. This is something to discuss with your doctor.
- Underlying Heart Conditions (Less Common): While less frequent, it’s important to note that a borderline ECG could sometimes hint at a more serious underlying heart condition. This emphasizes the importance of a thorough evaluation.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Help for Heart Issues
While dizziness on its own isn’t always an emergency, some symptoms demand immediate medical attention. Don’t hesitate to call emergency services or go to the nearest emergency room if you experience:
- Chest pain or pressure: This is a serious symptom and needs immediate evaluation.
- Severe shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing that’s suddenly severe requires urgent medical care.
- Fainting or near-fainting: Losing consciousness, even briefly, is concerning and needs to be checked out.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations) that feels alarming: If your heartbeat feels unusually fast, slow, or irregular and makes you anxious, seek medical attention.
Your health is your priority. Don’t delay seeking help if you’re worried.
Next Steps: Diagnostic Testing and Heart Evaluation
Your doctor will likely recommend some additional tests to better understand your borderline ECG and dizziness. These tests help paint a clearer picture of your heart’s health:
- Echocardiogram (Echo): This is like an ultrasound for your heart. It uses sound waves to create images of your heart’s structure and how well it’s pumping.
- Stress Test: This test monitors your heart’s activity while you exercise (usually on a treadmill). It helps identify problems that might only appear when your heart is working harder.
- Holter Monitor: This is a small, portable ECG device you wear for 24 to 48 hours. It records your heart’s rhythm continuously, providing a detailed look at your heart’s activity throughout the day.
- Blood Tests: Simple blood tests can check for electrolyte imbalances or other potential factors contributing to your symptoms.
Your doctor will determine which tests are most appropriate for your individual situation.
Lifestyle Tweaks for a Healthier Heart and Improved Well-being
Making some positive changes to your lifestyle can support your overall heart health and potentially help reduce dizziness. These aren’t quick fixes, but they’re important long-term habits:
- Diet: A balanced diet is key! Focus on plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Try to limit processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive salt.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens your heart and improves circulation. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
- Stress Management: Finding ways to manage stress is crucial for your heart health. Explore relaxation techniques like deep breathing, yoga, or meditation. A regular sleep schedule of 7-9 hours each night also aids in stress reduction.
- Hydration: Dehydration can lead to dizziness and affect heart rhythm. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day, more if you are active or in a hot environment.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Both alcohol and caffeine can trigger heart rhythm irregularities and exacerbate dizziness. Moderation is key.
Medications: Understanding the Role They Play in Cardiac Function
Some medications can influence your ECG and potentially contribute to dizziness. On the other hand, your doctor may prescribe medication to address any underlying issues revealed by further testing. Never start, stop, or change medications without first consulting your doctor. Be sure to inform your doctor of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are currently taking. Certain combinations can affect heart function.
Understanding Specific ECG Components: A Deeper Dive
To better understand your ECG results, it helps to know what the different parts of the ECG represent:
- P Wave: Represents atrial depolarization (the atria contracting). Abnormalities can indicate atrial enlargement or conduction problems. Normal duration is typically 80-120 milliseconds.
- QRS Complex: Represents ventricular depolarization (the ventricles contracting). Abnormalities can indicate ventricular hypertrophy, bundle branch blocks, or myocardial infarction. Normal duration is typically less than 120 milliseconds.
- T Wave: Represents ventricular repolarization (the ventricles relaxing). Abnormalities can indicate ischemia, electrolyte imbalances, or medication effects.
- PR Interval: Represents the time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles. Abnormalities can indicate AV blocks or pre-excitation syndromes. Normal duration is typically 120-200 milliseconds.
- QT Interval: Represents the total time for ventricular depolarization and repolarization. Abnormalities can indicate an increased risk of arrhythmias. Corrected QT interval (QTc) is typically less than 450 milliseconds in men and less than 460 milliseconds in women.
- ST Segment: Represents the period between ventricular depolarization and repolarization. Abnormalities can indicate ischemia or myocardial infarction.
Long-Term Management: Keeping Your Heart Healthy for Years to Come
Staying on top of your heart health is important, whether you’ve had a borderline ECG or not. Regular check-ups with your cardiologist will allow them to monitor your progress, make adjustments to your treatment plan if needed, and provide guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Consider keeping a heart health journal to track your symptoms, medications, diet, and exercise. This can be a valuable tool for your doctor to assess your progress and make informed decisions.
Potential Complications of Untreated Underlying Conditions
While a borderline ECG itself isn’t dangerous, ignoring it and any associated symptoms could lead to complications if an underlying condition exists. These complications could include:
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats can lead to palpitations, dizziness, fainting, or even sudden cardiac arrest.
- Heart Failure: The heart’s ability to pump blood effectively is compromised, leading to fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling.
- Stroke: Blood clots can form due to irregular heartbeats, leading to stroke.
- Coronary Artery Disease: Narrowing of the arteries can lead to chest pain, heart attack, or heart failure.
In Conclusion: Partnering with Your Doctor for Optimal Heart Health
A borderline ECG and dizziness suggest the need for a comprehensive evaluation. While it’s not necessarily a cause for immediate panic, it does require attention. By working closely with your healthcare provider, you can determine the cause of your symptoms and take proactive steps towards better heart health and reduced dizziness. Remember, open communication with your doctor is key. Don’t hesitate to ask questions, express your concerns, and actively participate in your care.
How to Interpret Borderline ECG Results with Varying
- Best Books on Meditation Recommended by Mindfulness Experts - January 30, 2026
- Best Mindfulness Books for Anxiety, Sleep, and Daily Peace - January 29, 2026
- Books On Mindfulness For A Happier, More Present Life - January 28, 2026