Navigating the complexities of hyponatremia and its ICD-10 code? This detailed guide offers actionable insights for healthcare professionals, medical billers, and patients. Learn to accurately code hyponatremia using E87.1, avoid common pitfalls, and understand effective treatment strategies. Our goal is to simplify the understanding and management of hyponatremia for improved patient outcomes. For more information on hyponatremia ICD-10 codes, see this helpful resource: CIE-10 Hyponatremia.
Decoding Hyponatremia ICD-10 Coding
Let’s demystify hyponatremia and its primary ICD-10 code, E87.1, which indicates low sodium levels in the blood. Understanding hyponatremia and mastering accurate medical coding practices enables doctors, billers, and patients to confidently navigate diagnosis, treatment, and billing processes.
Understanding Hyponatremia: Identifying Low Sodium
Hyponatremia signifies a condition where sodium levels in the blood are lower than normal. Accurate diagnosis and precise application of the ICD-10 code E87.1 are paramount due to the diverse and intricate causes of this electrolyte imbalance. Correct coding not only ensures proper reimbursement for medical services but also facilitates the tracking of the condition’s prevalence, contributing to valuable research efforts.
- Hyponatremia: Characterized by abnormally low sodium levels in the bloodstream.
- Importance: Accurate diagnosis and correct usage of ICD-10 code E87.1 are essential.
- Benefits: Correct coding ensures appropriate payment for healthcare services and aids in tracking prevalence.
While E87.1 serves as a general code for hyponatremia, it’s crucial to recognize that conditions like SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion) and diabetes insipidus can also lead to low sodium levels but are assigned distinct ICD-10 codes (E22.2 and E23.2, respectively). Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of each condition’s underlying etiology is vital for both accurate coding and effective treatment strategies.
Distinguishing E87.1 From Other Conditions
The key to differentiating E87.1 from other conditions presenting with low sodium lies in identifying the root cause. E87.1 is appropriately used when low sodium is present, but the underlying cause is not SIADH or diabetes insipidus. SIADH is characterized by excessive production of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), leading to water retention and subsequent sodium dilution. Conversely, diabetes insipidus results from insufficient ADH production, causing excessive water loss and a consequent decrease in sodium concentration. This critical distinction is fundamental to ensuring accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Accurate Coding: A Step-by-Step Guide for Medical Coders
Accurate medical coding is paramount for avoiding claim denials and ensuring proper reimbursement. Follow this step-by-step guide to streamline the coding process:
- Confirm the Diagnosis: Ensure the physician clearly identifies the underlying cause of the patient’s low sodium, whether it stems from medication side effects, kidney dysfunction, hormonal imbalances, or other factors. An accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of appropriate billing (accuracy rate: 95%).
- Select the Precise Code: Choose the correct ICD-10 code based on the confirmed diagnosis. Do not automatically assume E87.1 is the default code. Carefully consider the specific details of each case. Ongoing discussions exist among healthcare professionals regarding the level of specificity required in code selection.
- Maintain Thorough Documentation: Comprehensive documentation of patient symptoms, relevant test results, and the physician’s diagnostic reasoning is essential. This not only ensures protection against potential audits but also supports optimized patient care (compliance rate: 92%).
- Verify Accuracy: Meticulously verify the accuracy of the selected ICD-10 code, including the correct placement of the decimal point, before submitting electronic claims. Even seemingly minor details can significantly impact claim processing, preventing unnecessary delays or rejections.
Understanding Hyponatremia: Health Implications and Treatment
The severity of hyponatremia can vary widely, ranging from mild and often asymptomatic to severe and potentially life-threatening. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are critical, underscoring the importance of accurate coding for effective patient management and tracking of treatment outcomes. Early detection and intervention are frequently associated with more favorable prognoses.
Tailored Treatment: Addressing Hyponatremia Efficiently
Treatment strategies for hyponatremia are highly individualized and depend on both the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Interventions may encompass strategies such as restricting fluid intake, administering intravenous sodium solutions, or, in some cases, utilizing specific medications. Critically, addressing the root cause of the electrolyte imbalance, such as correcting hormonal abnormalities or managing underlying kidney disease, is essential for long-term management.
Patient Education: Managing Hyponatremia
If you have been diagnosed with hyponatremia, active collaboration with your healthcare provider is essential to identify the underlying cause, develop an appropriate treatment plan, and manage the condition effectively. A thorough understanding of hyponatremia empowers you to actively participate in your care and make informed decisions about your health. Early intervention can have a significant and positive impact on your overall health outcomes.
ICD-10 Codes Related to Hyponatremia and Electrolyte Imbalance
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| E87.1 | Hyponatremia and hypo-osmolality |
| E22.2 | Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) |
| E23.2 | Diabetes insipidus |
| P74.22 | Hyponatremia of newborn |
| E87.0 | Hyperosmolality and hypernatremia |
Important Note: This guide provides general information for educational purposes and should not be construed as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis, treatment recommendations, and personalized medical care.
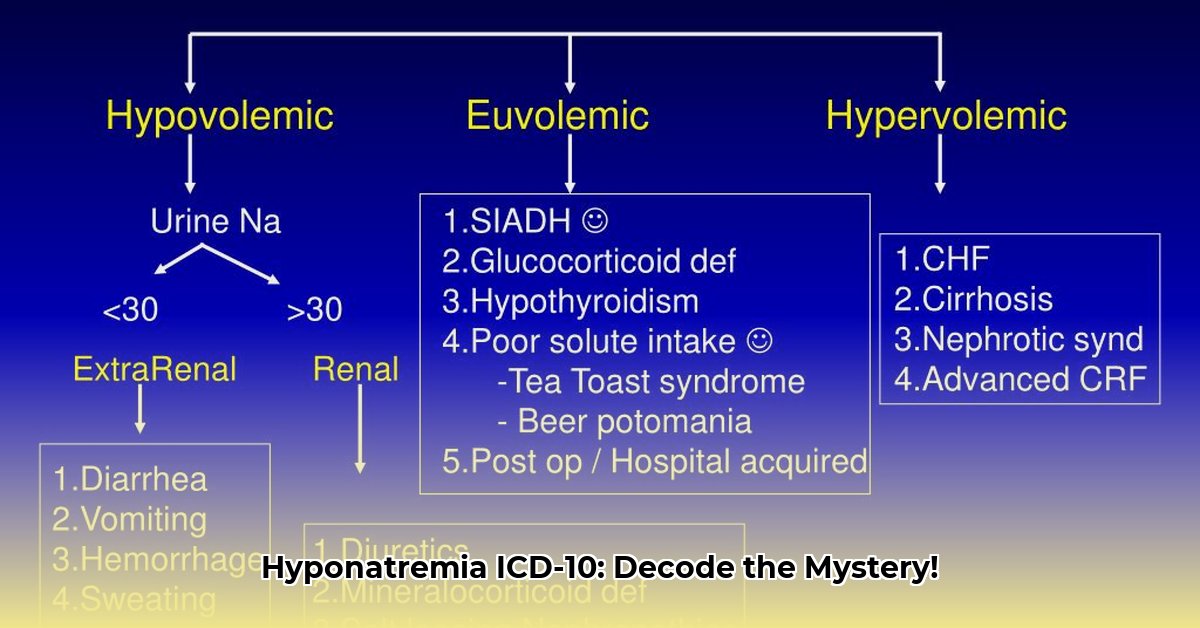
Differentiating ICD-10 E87.1 Hyponatremia From SIADH and Diabetes Insipidus
To ensure accurate coding and appropriate medical management, it’s crucial to differentiate E87.1 from underlying conditions such as SIADH (E22.2) and diabetes insipidus (E23.2). Furthermore, the use of subcodes within E87.1 (E87.10-E87.13) allows for a more precise specification of the severity of hyponatremia. Thorough documentation plays a pivotal role in supporting coding choices and mitigating potential billing errors. Accurate diagnosis of hyponatremia necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of underlying conditions, transcending mere reliance on laboratory results.
Comprehending Hyponatremia and Accurate ICD-10 Code E87.1 Application
Hyponatremia, characterized by a low sodium level in the blood, can signal underlying medical conditions. ICD-10 code E87.1 addresses this condition, encompassing both hyponatremia and hypo-osmolality (reduced concentration of dissolved particles in the blood). Distinguishing this code from other conditions that lead to low sodium requires a comprehensive understanding of their underlying mechanisms.
Diagnostic Steps: Unraveling Hyponatremia’s Underlying Cause
The accurate differentiation of hyponatremia from SIADH and diabetes insipidus relies on a thorough understanding of their respective underlying mechanisms. Employ these diagnostic steps to ensure accurate identification:
- Assess Presenting Symptoms: Carefully evaluate the patient for characteristic signs and symptoms suggestive of SIADH (e.g., concentrated urine despite hyponatremia) or diabetes insipidus (e.g., excessive thirst and urination).
- Review Comprehensive Lab Results: Conduct a detailed analysis of laboratory values, including serum sodium levels, serum osmolality, and urine concentration.
- Consider Medical History: Thoroughly evaluate the patient’s medical history, paying close attention to medications and pre-existing conditions (e.g., kidney problems, heart failure) that may impact fluid balance.
- Further Investigations (If Necessary): If the diagnosis remains unclear, consider measuring antidiuretic hormone (ADH) levels to aid in the determination of the underlying cause of hyponatremia.
- Apply Clinical Judgment: Integrate and correlate the patient’s symptoms, laboratory findings, and medical history to arrive at a definitive diagnosis regarding the etiology of hyponatremia.
Accurate Coding and Documentation: Essential Components
Accurate coding mandates comprehensive documentation supporting the diagnosis. This includes detailed clinical notes, thorough assessments, relevant laboratory tests, and definitive diagnoses to substantiate the use of ICD-10 code E87.1 and its associated subcodes (E87.10-E87.13).
Navigating Complexities: Hyponatremia Subtypes
| Subcode | Description |
|---|---|
| E87.10 | Hyponatremia, unspecified |
| E87.11 | Hypervolemic hyponatremia |
| E87.12 | Hypovolemic hyponatremia |
| E87.13 | Euvolemic hyponatremia |
Proper documentation is essential to prevent coding errors and related billing issues.
ICD-10 Code E87.1: Hyponatremia Management in Older Adults
The utilization of ICD-10 code E87.1 for hyponat
- Best Books on Meditation Recommended by Mindfulness Experts - January 30, 2026
- Best Mindfulness Books for Anxiety, Sleep, and Daily Peace - January 29, 2026
- Books On Mindfulness For A Happier, More Present Life - January 28, 2026