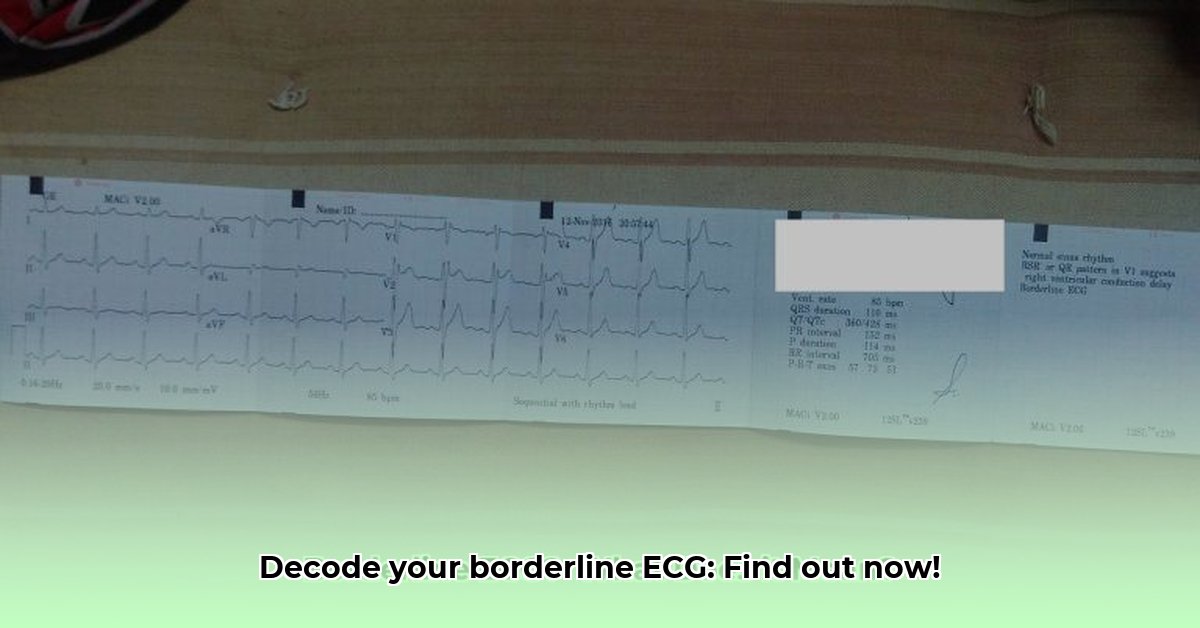
Your heart’s rhythm, a complex and vital process, is meticulously monitored by an electrocardiogram (ECG). Borderline ECGs, characterized by rhythms that deviate slightly from the norm but are not definitively abnormal, can often be a source of confusion. For more detailed information on next steps, see this helpful guide: Next Steps. This guide aims to clarify the causes, implications, and necessary actions associated with borderline ECG findings, making it an invaluable resource for both patients and healthcare professionals. It empowers you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the complexities of ambiguous ECG results.
Recognizing Borderline ECGs: Understanding the Nuances
Borderline ECG results can be unsettling, often described as an “inconclusive” finding. Unlike a normal ECG, which clearly indicates healthy heart function, or an abnormal ECG, which points to a specific cardiac issue, a borderline ECG falls into a gray area. It suggests that there may be some irregularities in your heart’s electrical activity, but these irregularities are not significant enough to warrant a definitive diagnosis. The crucial point is understanding the implications for you. While a borderline result may indicate a minor issue, it could also suggest something more serious that requires prompt addressing.
Demystifying Borderline ECGs: What They Really Mean
Your electrocardiogram (ECG) meticulously records the electrical activity of your heart, providing valuable information about both its rate and rhythm. A “normal” ECG displays a consistent, predictable pattern, indicating proper heart function, while a “borderline” reading falls within the ambiguous gray area between normal and clearly abnormal. This ambiguity necessitates further investigation to ascertain the underlying cause and determine the best course of action.
Exploring Potential Causes of Borderline ECG Results
Several factors can contribute to borderline ECG results, making accurate interpretation a complex process. Stress and anxiety, common in today’s fast-paced world, can trigger temporary changes in heart rhythm, leading to borderline findings. Electrolyte imbalances, such as deficiencies in potassium, magnesium, or calcium, which are essential for proper electrical signaling in the heart, can also manifest as borderline ECG readings. Furthermore, certain medications, including some antidepressants and antihistamines, may temporarily alter heart rhythm, affecting ECG results. Crucially, early indicators of underlying cardiovascular conditions, such as hypertension or coronary artery disease, can sometimes subtly manifest as anomalies on an ECG, highlighting the importance of thorough evaluation. Other potential causes can include:
- Caffeine Intake: Excessive caffeine consumption can stimulate the heart and lead to minor rhythm changes.
- Nicotine Use: Nicotine can also affect heart rate and rhythm, potentially resulting in a borderline ECG.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can disrupt electrolyte balance and influence heart function.
- Body Position: The position of your body during the ECG test can sometimes affect the readings.
- Technical Errors: In rare cases, improper electrode placement or machine malfunction can contribute to inaccurate results.
Actionable Intelligence: Navigating Borderline ECG Findings
Receiving a borderline ECG result should be approached with informed action, not panic. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Consult Your Doctor: The first and most crucial step is to schedule an appointment with your doctor to discuss the results in detail. During this consultation, provide a comprehensive health history, including any existing medical conditions, family history of heart disease, and a detailed account of any symptoms you may be experiencing, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness. Be sure to also share relevant lifestyle information, including your diet, exercise habits, smoking status, and alcohol consumption, to provide a clearer clinical picture.
- Potential Additional Testing: Based on your individual situation, risk factors, and the details revealed during your consultation, your doctor may recommend further testing to obtain a more accurate diagnosis and rule out any serious underlying conditions. These tests may include:
- Stress Test: A stress test evaluates your heart’s function while you exercise, helping to identify any limitations in blood flow.
- Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves to create a detailed image of your heart’s structure and function.
- Holter Monitor: A Holter monitor is a portable device that continuously records your heart rhythm over 24-48 hours, capturing intermittent irregularities that may not be detected during a standard ECG.
- Event Recorder: An event recorder is similar to a Holter monitor but is worn for a longer period (up to 30 days) and is activated only when you experience symptoms.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help assess electrolyte levels, thyroid function, and other factors that may be contributing to your borderline ECG.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regardless of the underlying cause, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is always beneficial. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a balanced diet low in saturated fat and sodium, stress management techniques, and smoking cessation.
- Medication Review: Your doctor will carefully review your current medications, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and supplements, to identify any potential culprits that may be contributing to heart rhythm alterations. If necessary, adjustments will be made to ensure safe and effective interaction and to avoid potential adverse effects.
Long-Term Management: Living with Borderline ECG Results
Long-term management strategies are determined by the root cause of the borderline results and your overall health profile, necessitating a thorough discussion with your physician to develop a personalized plan.
- Routine Check-ups: Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are crucial for ongoing monitoring and risk assessment. These check-ups may include periodic ECGs, blood tests, or other diagnostic evaluations to track your heart health over time. The frequency of these check-ups will be tailored to your unique needs and risk factors.
- Risk Stratification: Your doctor will utilize the information gathered from your test results, medical history, and lifestyle factors to assess your individual risk of developing future heart problems. This comprehensive assessment will allow for the development of a personalized management plan that addresses your specific needs and concerns.
- Personalized Treatment Strategy: Collaborate closely with your doctor to create a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses any identified underlying issues and supports overall heart health. This plan may encompass a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medication management, and ongoing monitoring.
Addressing the Limitations of Automated ECG Interpretations
Automated ECG interpretations provide valuable initial assessments, but they are not without limitations. Many ECGs are incorrectly flagged as “borderline” due to inherent limitations in the algorithms used by these machines. This highlights the critical importance of relying on the expertise of a qualified cardiologist to interpret ECG findings within the context of your individual medical history, symptoms, and risk factors. The machine provides data, but the doctor provides crucial context and clinical judgment.
Causes and Interventions: A Quick Reference
| Potential Cause | Possible Doctor’s Response |
|---|---|
| Electrolyte Imbalances | Dietary changes, electrolyte supplements, medication adjustments to address underlying causes (e.g., kidney problems) |
| Stress/Anxiety | Stress management strategies (therapy, relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation), possibly medication for anxiety |
| Underlying Heart Conditions | Further testing (stress test, echocardiogram, cardiac catheterization), medication to manage specific conditions, lifestyle changes (diet, exercise) |
| Medication Side Effects | Medication adjustment or change to an alternative drug with fewer cardiac side effects, careful monitoring for any adverse effects of current medications |
| High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) | Lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, weight management), medication to lower blood pressure, regular monitoring |
Remember, a borderline ECG does not automatically mean you have a serious heart problem requiring immediate intervention. It does, however, necessitate close collaboration with your doctor to identify the underlying cause and take appropriate steps to protect and optimize your heart health. Don’t hesitate to ask clarifying questions and actively participate in the decision-making process.
How to Interpret Borderline ECG Results and Next Steps
Core Insights:
- Borderline findings suggest subtle cardiac rhythm irregularities, but are not definitive diagnoses of heart disease.
- Ruling out serious conditions or identifying contributing factors requires further investigations and careful clinical judgment.
- The urgency of follow-up is critical and should be determined based on individual patient symptoms, risk factors, and overall clinical presentation.
Deciphering the Subtleties: What Does “Borderline” Really Mean?
A borderline ECG result is often not a clear indicator of heart disease and can be likened to examining a slightly blurry photograph – you can discern something, but the details lack sharpness. The ECG reveals slight deviations from the typical heart rhythm, which can stem from a multitude of factors. It’s highly recommended that you seek further evaluation to address any potential uncertainties and ensure accurate diagnosis.
Understanding the Causes: Why These Borderline Results?
A myriad of factors can contribute to borderline ECG results, including electrolyte imbalances, medication side effects, stress, and anxiety. A comprehensive understanding of the patient’s overall health context is crucial, as the underlying cause can sometimes be quite simple and easily addressed. While there’s usually no need for immediate alarm, it’s always prudent to investigate further to rule out any potential underlying issues.
How to Interpret Borderline ECG Results and Next Steps: The Practical Approach
Here’s a structured approach for you—or your doctor—to effectively address borderline ECG findings:
- Evaluate the Complete Clinical Picture: Your doctor will thoroughly consider your symptoms (chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations), medical history, and risk factors (
- Mindfulness Exercises For Anxiety PDF To Reduce Stress - February 26, 2026
- Mindfulness Activities for Adults PDF for Stress Relief - February 25, 2026
- Mindfulness Techniques PDF Offers Free Exercises for Calm and Focus - February 24, 2026