Receiving a “borderline” Electrocardiogram (ECG) result can understandably cause anxiety. It signifies that the test detected some deviations from the norm, but the implications aren’t immediately clear. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the concept of a borderline ECG, explaining its potential causes, the importance of further investigations, and the steps you and your healthcare provider should take to ensure appropriate care. We’ll translate complex medical jargon into accessible language, empowering you to feel informed and proactive in managing your heart health.
Demystifying Borderline ECG: What It Really Means
A borderline ECG result falls into a gray area between “normal” and “abnormal,” creating uncertainty for both patients and physicians. Instead of being a definitive diagnosis, it acts as a prompt for further evaluation. Let’s delve into the common causes of borderline ECGs and emphasize the significance of comprehensive assessment.
The Borderline ECG: A Subtle Signal
Visualize your heart as an intricate electrical system, and an ECG as a snapshot of its activity. Think of a borderline result as a slightly out-of-tune instrument in an orchestra – not a complete disruption, but something requiring attention. It’s crucial to understand that a borderline ECG doesn’t automatically equate to a serious heart condition. Instead, it indicates the necessity for a more in-depth investigation to uncover the underlying cause. These readings often reflect minor variations in the heart’s electrical signals, demanding careful interpretation.
Numerous factors can lead to a borderline ECG reading. These factors can be broadly classified into the following categories:
1. Technical Artifacts: In some instances, the issue might stem from the test itself. Improper electrode placement or even slight movements during the procedure can introduce inaccuracies. External electrical interference can also distort the readings. Fortunately, repeating the ECG with meticulous attention to detail often resolves these discrepancies.
2. Electrolyte Fluctuations: The heart’s rhythm relies heavily on a delicate balance of electrolytes, including minerals like potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium. Imbalances in these minerals, triggered by dehydration, kidney problems, or specific medications, can manifest as borderline changes on the ECG. Correcting these imbalances often rectifies the ECG readings.
3. Potential Underlying Heart Conditions: A borderline ECG may, in some cases, suggest the presence of a developing or mild heart condition. This could include conditions like ischemia (insufficient blood flow to the heart) or early-stage arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats). While many borderline ECGs don’t indicate serious heart issues, it’s crucial to investigate further to rule out such possibilities.
4. Medication Influence: Certain medications, particularly those affecting heart rhythm or electrolyte levels, can influence ECG results, potentially leading to a borderline reading. This effect is often temporary and resolves upon adjusting or discontinuing the medication.
5. The Impact of Stress and Anxiety: The connection between mind and body is undeniable. Significant stress or anxiety can temporarily alter heart rhythm, sometimes resulting in a borderline ECG that returns to normal once the individual is calmer. The importance of stress-reduction techniques for cardiovascular health should not be underestimated. Studies show that mindfulness practices can significantly improve heart rate variability and reduce blood pressure.
Following Up: Further Investigations
A borderline ECG isn’t a medical emergency, but it does necessitate further investigation. Your physician will likely recommend additional tests based on your unique circumstances, including your symptoms, medical history, and the specific characteristics of your ECG. These investigations might include:
- Repeat ECG: This simple step helps eliminate any technical errors that might have influenced the initial reading.
- Blood Tests: Analyzing electrolyte levels can help identify any imbalances that may be contributing to the borderline ECG.
- Holter Monitor: This portable device continuously records your heart’s rhythm over a period of 24 to 48 hours. It’s particularly useful for detecting intermittent arrhythmias that may not be apparent during a standard ECG.
- Stress Test: This test assesses your heart’s response to exercise, revealing potential problems that might not be evident at rest. It helps determine if there is any limitation of blood supply to the heart muscle during activity.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of your heart, providing detailed images of its structure and function, allowing doctors to identify potential issues such as valve abnormalities or heart muscle dysfunction.
Taking Control: Your Next Steps
For Patients:
- Stay Calm: A borderline ECG is a reason for further evaluation, not immediate panic.
- Schedule a Timely Follow-Up: Make an appointment with your physician as soon as possible to discuss the results and plan the next steps.
- Provide Comprehensive Information: Be prepared to share detailed information about your symptoms, medications, lifestyle, and stress levels with your doctor.
- Adhere to Medical Advice: Carefully follow your doctor’s recommendations, whether they involve additional tests, lifestyle modifications, or medication adjustments.
For Healthcare Professionals:
- Analyze the ECG Thoroughly: Carefully examine the ECG tracing, paying attention to even subtle deviations from the norm.
- Obtain a Detailed Patient History: Gather comprehensive information about the patient’s medical history, medication use, and any symptoms they might be experiencing.
- Order Appropriate Diagnostic Tests: Select the most appropriate additional diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause of the borderline ECG.
- Communicate Clearly: Clearly explain the findings, potential causes, and the plan for further investigation to the patient.
Collaborating Towards Clarity: A Team Effort
Remember, a borderline ECG is not a final diagnosis but rather a piece of a larger puzzle. By collaborating closely with your healthcare provider and undergoing any recommended tests, you can gain a clearer understanding of your heart health. This collaborative process will help determine whether the borderline ECG is due to a technical error, a medication side effect, or an underlying condition that requires further attention.
Key Takeaways:
- Borderline ECG results are inconclusive and warrant further evaluation.
- Various factors can contribute to borderline ECG findings, including electrolyte imbalances and underlying heart conditions.
- Interpreting borderline ECG results and determining the necessary follow-up tests involves careful consideration of the patient’s medical history and clinical presentation.
- Additional diagnostic tests help clarify the ECG findings and guide treatment decisions.
- Prompt follow-up with a healthcare professional is essential.
Deciphering the ECG Enigma: Dissecting the Meaning of “Borderline”
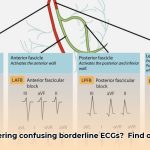
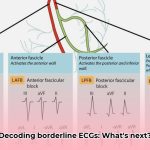
An electrocardiogram (ECG) serves as a fundamental test for assessing the heart’s rhythm and electrical function. When an ECG reveals results that are not definitively normal or abnormal, they are categorized as “borderline.” This doesn’t automatically indicate a serious health problem, but it does signal the need for further investigation. A borderline ECG can be likened to a slightly blurred image, where the overall subject is visible, but the finer details remain indistinct, necessitating further scrutiny. What specific patterns within borderline ECGs merit heightened medical attention?
Unveiling Potential Causes: Identifying Culprits Behind Borderline ECGs
Numerous factors can contribute to a borderline ECG reading. Electrolyte imbalances, such as deficiencies in potassium or magnesium, can disrupt the heart’s electrical signals, leading to inconclusive results. Both physical and emotional stress can also transiently affect heart rhythm. Medications, known to influence heart rate or rhythm, represent another potential cause. While not always immediately evident, underlying heart conditions can also manifest as borderline ECG findings. Lastly, technical issues during the ECG recording itself can contribute to a borderline interpretation.
The Diagnostic Process: Determining Necessary Tests
In the event of a borderline ECG, your physician might suggest additional tests to gain a more comprehensive understanding. These tests may include:
- Repeat ECG: A simple repeat ECG can sometimes clarify any ambiguities present in the initial reading.
- Holter Monitor: This portable device records your heart’s rhythm continuously over a 24-48 hour period, distinguishing between temporary anomalies and more persistent issues.
- Exercise Stress Test: This test evaluates your heart’s response to physical exertion, uncovering any problems that might only manifest under stress.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound provides detailed images of the heart’s structure and function, assessing its overall health and integrity.
- Cardiac MRI: This advanced imaging technique is employed to identify structural (anatomic) heart defects that may not be apparent through other means.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are conducted to assess electrolyte levels and detect markers indicative of cardiac damage.
A Patient-Centric Approach: Navigating the Next Steps
Upon receiving a borderline ECG result, it’s crucial to avoid unnecessary anxiety. The most important step is to adhere to your physician’s recommendations and schedule a follow-up appointment. They will thoroughly review your results, assess your overall health status, and determine whether further investigation is warranted. Your physician will provide a detailed explanation of the results and guide you through the necessary next steps. Open communication is paramount in addressing any concerns related to your heart health. How can patients actively collaborate with healthcare providers to effectively interpret and manage borderline ECG findings?
Healthcare Professionals: Interpreting Ambiguity
Interpreting borderline ECGs demands extensive experience and sound clinical judgment. The process involves a meticulous review of the ECG tracing, taking into account the patient’s medical history and presenting symptoms. It’s essential to correlate the findings with other relevant clinical information. A multi-faceted approach often provides clarity. Remember to involve patients in shared decision-making, ensuring they fully understand the implications of their results. Carefully weigh the benefits and risks when considering additional tests.
- Mindfulness Exercises For Anxiety PDF To Reduce Stress - February 26, 2026
- Mindfulness Activities for Adults PDF for Stress Relief - February 25, 2026
- Mindfulness Techniques PDF Offers Free Exercises for Calm and Focus - February 24, 2026