Low sodium in your blood, called chronic hyponatremia, might not sound serious, but it can really affect how you feel. It can cause everything from tiredness to more serious problems with your brain. For more information on hyponatremia symptoms, see this helpful resource: Hyponatremia Symptoms. This guide will help you understand what’s happening, what to watch out for, and how to best manage it. We’ll explain the causes, common mistakes to avoid, and give you simple steps to take control. We’ll also provide tips to prevent problems and keep you feeling your best. Whether you’re looking for answers, support, or just want to learn more, this guide is here to help you.
Chronic Hyponatremia: Understanding, Identifying, and Managing Low Sodium Levels
Are you aware that persistent headaches, muscle weakness, and even subtle changes in mental clarity can be potential signs of chronic hyponatremia? This condition, characterized by a prolonged state of low sodium in the blood, demands a comprehensive understanding and proactive management approach for sustained well-being.
Feeling persistently tired, battling nagging headaches, experiencing unexplained muscle weakness, or noticing subtle shifts in your cognitive function? These could be indicators of chronic hyponatremia – a condition marked by insufficient sodium levels in your blood. While it might not initially seem alarming, understanding its nature and adopting appropriate management strategies are essential. Let’s delve into this often-underestimated health concern.
Recognizing the Signs: Identifying Symptoms of Chronic Hyponatremia
Chronic hyponatremia signifies that your sodium levels have been consistently low over an extended duration, rather than a sudden decline. Given its gradual development, the symptoms often emerge subtly and progressively. Visualize it as a slow leak in a tire – the gradual loss of pressure might go unnoticed until the tire is significantly deflated.
Common early warning signs include:
- Persistent Fatigue: Experiencing persistent tiredness that defies your best efforts to rest, even after adequate sleep? It could be a significant clue.
- Recurrent Headaches: Persistent headaches, particularly if they exhibit resistance to over-the-counter pain relievers, warrant medical evaluation.
- Nausea: Experiencing a recurring queasy sensation or frequent upset stomach? It may present as a pertinent symptom.
- Muscle Weakness and Cramps: Notice a decline in your customary strength or stamina, accompanied by involuntary muscle contractions? This warrants prompt attention.
- Cognitive Impairment: Experiencing alterations in cognitive function, such as memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, or impaired decision-making capabilities? These symptoms may warrant evaluation.
- Mood Swings or Confusion: Experiencing abrupt shifts in personality or encountering difficulties in maintaining focus? These changes could signify an underlying issue.
- Gait Disturbances: Experiencing unsteadiness or imbalance while walking, potentially leading to falls? It’s prudent to seek medical evaluation.
More severe symptoms, which require immediate medical attention, include:
- Seizures: Experiencing uncontrolled muscle spasms or convulsions constitutes a serious clinical indication.
- Loss of Consciousness: This represents a medical emergency mandating immediate intervention.
The severity of symptoms depends on the extent of sodium level reduction and the rate at which it occurs. It’s crucial to recognize that these symptoms are not exclusive to hyponatremia; they can overlap with various other medical conditions. Therefore, obtaining a diagnosis from a qualified healthcare professional is imperative.
Understanding the Causes: Exploring the Origins of Chronic Hyponatremia
Do you know that kidney dysfunction, specific medications, hormonal imbalances, and underlying health conditions can contribute to the development of chronic hyponatremia? Identifying these potential causes is crucial for timely intervention and customized management strategies.
The kidneys play a central role in maintaining sodium equilibrium. They diligently regulate sodium levels in your bloodstream. Disruptions to this delicate balance can precipitate hyponatremia.
Various factors can disrupt this equilibrium:
- Kidney Dysfunction: Impaired kidney function can compromise the effective regulation of sodium levels.
- Medications: Certain prescription drugs, including diuretics (water pills), antidepressants, and pain medications, can interfere with sodium regulation. It’s crucial to discuss all medications with your healthcare provider.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions such as syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), and adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease) can disrupt sodium balance.
- Underlying Health Problems: Conditions such as congestive heart failure (where the heart struggles to pump effectively), liver cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), and certain cancers can lead to fluid retention, diluting sodium concentrations.
- Excessive Water Intake: Consuming excessive amounts of water, particularly without adequate electrolyte replenishment, can dilute sodium levels in the bloodstream. This is particularly relevant for athletes engaging in endurance events.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like primary polydipsia (excessive thirst), diarrhea, and vomiting can lead to sodium loss and subsequent hyponatremia.
It’s essential to address the underlying cause, not just manage the symptoms. Your healthcare provider will conduct thorough investigations to pinpoint the underlying factors contributing to the imbalance.
Diagnosing the Issue: Methods for Detecting Chronic Hyponatremia
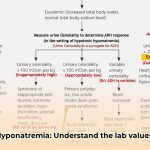
Are you aware that blood tests, urine tests, and comprehensive medical evaluations are essential for diagnosing chronic hyponatremia? Timely and accurate diagnosis forms the basis for effective treatment planning.
The primary diagnostic step involves a straightforward blood test to ascertain your sodium levels. Additionally, your healthcare provider will conduct a thorough medical history, inquiring about your symptoms, medications, and any underlying health conditions. Based on these findings, further diagnostic tests may be warranted:
- Blood Tests: Additional blood tests may assess kidney function, electrolyte balance, hormone levels, and overall health status.
- Urine Tests: These assist in evaluating kidney function and electrolyte balance, providing insights into the underlying cause of hyponatremia.
- Fluid Deprivation Test: In certain cases, a fluid deprivation test may be conducted to assess the body’s ability to concentrate urine and conserve sodium.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging modalities such as ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs may be employed to visualize the kidneys, heart, or liver, contingent upon the suspected underlying cause.
Obtaining an accurate diagnosis is essential for formulating an effective treatment strategy. Avoid delaying seeking medical attention if you suspect a problem.
Managing Chronic Hyponatremia: Tailored Treatment Strategies
Did you know that treatment for chronic hyponatremia entails a gradual restoration of sodium levels while addressing the underlying cause? A customized approach ensures the most favorable outcomes.
Treating chronic hyponatremia involves a gradual and careful restoration of sodium levels to the normal range while concurrently addressing the underlying cause. Rapid corrections can be hazardous, necessitating a measured approach. Treatment plans are individualized, factoring in your specific needs and medical history.
Various treatment modalities may be employed:
- Fluid Restriction: In cases of excessive fluid volume diluting sodium concentrations, your healthcare provider may advise limiting daily fluid intake.
- Medication Adjustments: If medications contribute to hyponatremia, adjustments to dosage, medication changes, or discontinuation may be necessary, under medical supervision.
- Dietary Modifications: In select instances, dietary adjustments, including sodium intake optimization, may support sodium level regulation. This should always be executed under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
- Medications: Medications such as vasopressin receptor antagonists (vaptans) may be prescribed in specific cases to promote water excretion and elevate sodium levels.
- Intravenous (IV) Sodium Chloride: In severe cases, IV sodium chloride solutions may be administered cautiously to augment sodium levels under close monitoring.
Patience and consistent monitoring are paramount throughout the treatment process.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Are you aware that severe confusion, seizures, or loss of consciousness necessitate immediate medical intervention for individuals with chronic hyponatremia? Recognizing these critical warning signs is essential for prompt action.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following severe symptoms:
- Profound Confusion or Disorientation
- Seizures
- Loss of Consciousness
- Severe Muscle Weakness
- Difficulty Breathing
These symptoms may indicate a life-threatening situation.
Living with Chronic Hyponatremia: Long-Term Management
Did you know that regular monitoring, adherence to treatment plans, lifestyle modifications, and effective communication with your healthcare provider are pivotal for long-term chronic hyponatremia management? Proactive engagement in managing your condition ensures optimal well-being.
Living with chronic hyponatremia necessitates ongoing monitoring and adherence to your healthcare provider’s recommendations. This may entail regular blood tests to monitor sodium levels and ensure stability. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, encompassing a balanced diet, regular exercise (as advised by your healthcare provider), and stress management techniques, is crucial. Open communication with your healthcare provider is essential for continuous management and addressing any concerns.
Potential Complications of Untreated Hyponatremia
Are you aware that neglecting chronic hyponatremia can lead to severe complications, including brain swelling, neurological damage, seizures, coma, and even mortality? Early detection and appropriate treatment can prevent devastating outcomes.
Failure to address chronic hyponatremia can have serious and potentially life-threatening consequences:
- Brain Swelling (Cerebral Edema): The brain is highly sensitive to sodium fluctuations, rendering it susceptible to swelling.
- Neurological Damage: Prolonged hyponatremia can induce permanent neurological damage, affecting cognitive and motor functions.
- Seizures: Severe
- Best Books on Meditation Recommended by Mindfulness Experts - January 30, 2026
- Best Mindfulness Books for Anxiety, Sleep, and Daily Peace - January 29, 2026
- Books On Mindfulness For A Happier, More Present Life - January 28, 2026