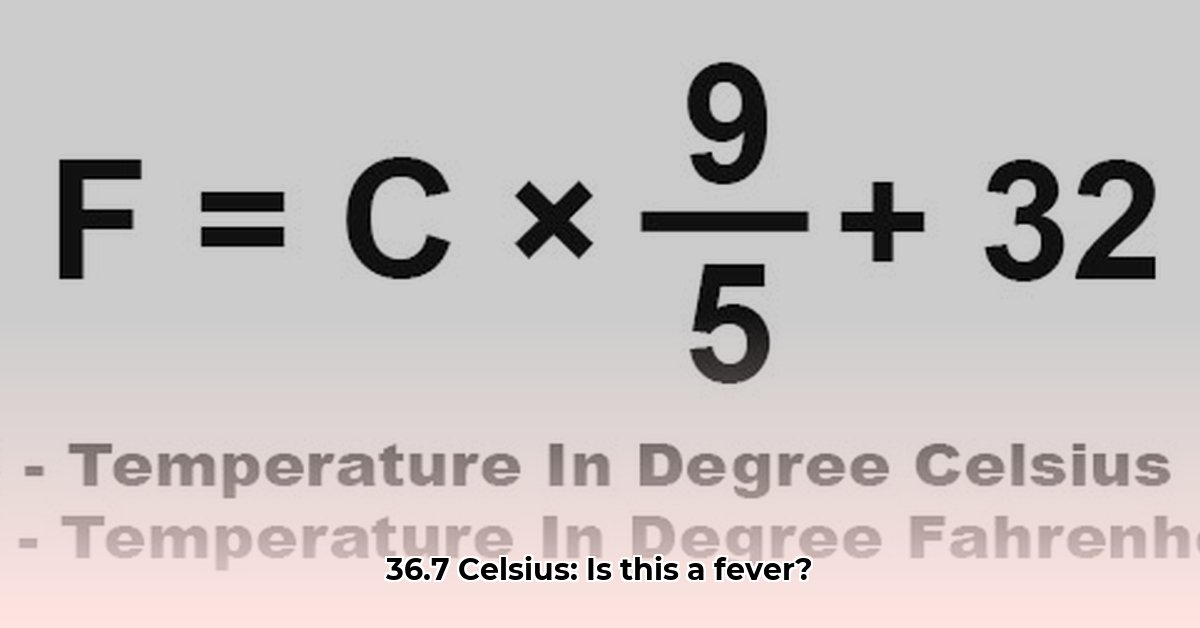Instant Answer
36.7°C is equal to 98.06°F.
Understanding the Conversion
The conversion from Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F) follows a standard formula:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Step-by-Step Calculation for 36.7°C
- Multiply: 36.7 × 9/5 = 66.06
- Add: 66.06 + 32 = 98.06°F
Visual Aid
Celsius (°C) --> x 9/5 --> + 32 --> Fahrenheit (°F)
36.7 --> 66.06 --> 98.06
Real-World Significance
36.7°C (98.06°F) is close to the average normal human body temperature. However, it’s important to note that “normal” body temperature can vary slightly based on factors like time of day, activity level, age, and individual differences. Some studies suggest that the average might actually be slightly lower than the commonly cited 98.6°F (37°C). Ongoing research continues to explore these variations.
Celsius vs. Fahrenheit: Different Scales, Same Measurement
Both Celsius and Fahrenheit measure temperature, but they use different scales. Celsius, also known as centigrade, sets the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point at 100°C. Fahrenheit uses 32°F for freezing and 212°F for boiling. These different scales arose from different historical contexts and scientific conventions.
Temperature Comparisons
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 32 | Freezing Point of Water |
| 10 | 50 | A Chilly Day |
| 20 | 68 | Mild, Pleasant Weather |
| 25 | 77 | Comfortable Room Temperature |
| 30 | 86 | Warm, Summer-like Weather |
| 36.7 | 98.06 | Near Average Body Temperature |
| 37 | 98.6 | Average Body Temperature |
| 40 | 104 | High Fever |
| 100 | 212 | Boiling Point of Water |
Note: These are average values. Individual experiences can vary.
Beyond Celsius and Fahrenheit
While Celsius and Fahrenheit are the most common temperature scales, scientists and engineers often use Kelvin (K) and, less frequently, Rankine (°R). These are absolute temperature scales, meaning their zero point is absolute zero, the theoretically lowest possible temperature where all molecular motion ceases.
| Scale | Symbol | Absolute Zero | Freezing Point of Water | Boiling Point of Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celsius | °C | -273.15°C | 0°C | 100°C |
| Fahrenheit | °F | -459.67°F | 32°F | 212°F |
| Kelvin | K | 0 K | 273.15 K | 373.15 K |
| Rankine | °R | 0°R | 491.67°R | 671.67°R |
Kelvin is particularly important in scientific calculations because it directly relates to the thermal energy of a system. Converting between Celsius and Kelvin is straightforward: K = °C + 273.15.
The Future of Temperature Measurement
Research in areas like thermodynamics and materials science constantly refines our understanding of temperature and its measurement. This ongoing exploration may lead to even more precise measurement techniques, especially at extreme temperatures, and potentially even new temperature scales in the future. While the fundamental principles remain consistent, the pursuit of deeper understanding continues.
Uncertainty and Precision
It’s crucial to remember that all temperature measurements, including the conversion from 36.7°C to 98.06°F, have inherent uncertainties. Thermometer calibration, environmental factors, and the very nature of measuring a physical quantity introduce potential variations. While we strive for accuracy, acknowledging these limitations provides a more nuanced perspective on temperature and its measurement.
- Best Mindfulness Books for Anxiety, Sleep, and Daily Peace - January 29, 2026
- Books On Mindfulness For A Happier, More Present Life - January 28, 2026
- Essential Meditation Books for Beginners and Experienced Practitioners - January 27, 2026