Receiving a borderline ECG result can be confusing and concerning. This guide provides a clear understanding of what a borderline ECG means, its potential causes, and recommended next steps. We’ll break down the information in an accessible manner, empowering you to make informed decisions about your heart health. For more in-depth information on next steps, see this helpful guide: Next Steps After ECG.
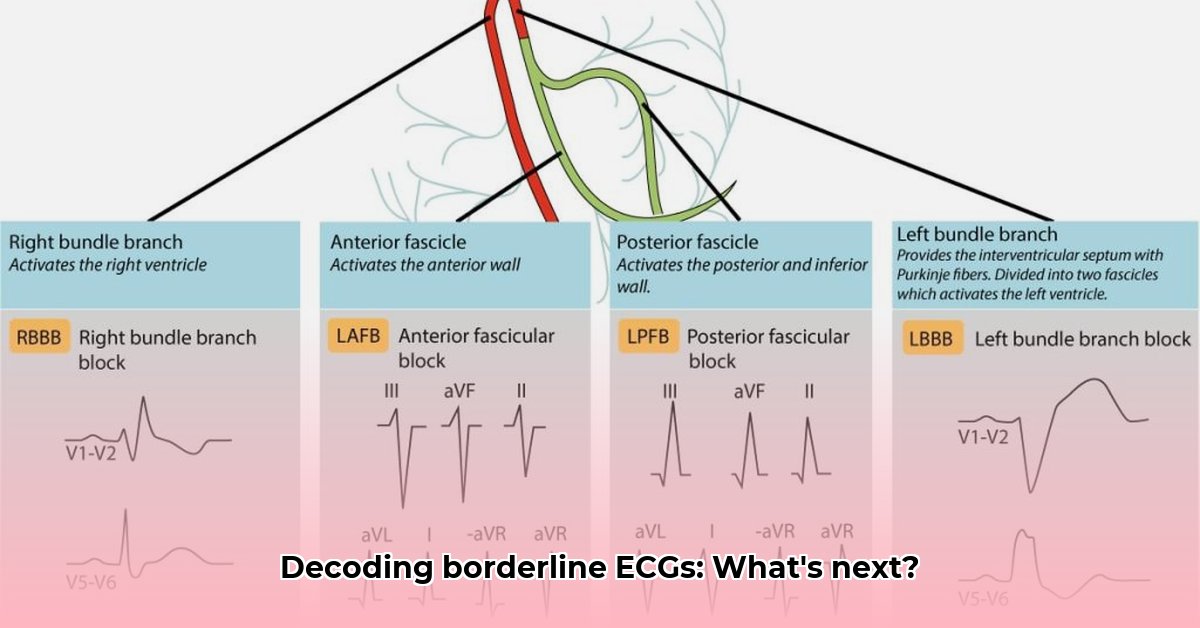
What is a Borderline ECG?
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of your heart. It’s a valuable tool for detecting various heart conditions. A borderline ECG indicates that the test results aren’t definitively normal or abnormal. Some aspects of the ECG tracing fall within the normal range, while others show slight deviations. This “gray area” necessitates further investigation.
A borderline ECG result is not a diagnosis. It simply suggests that there are subtle irregularities in your heart’s electrical activity that warrant further evaluation.
Why Further Investigation is Necessary
The ambiguity of a borderline ECG underscores the importance of additional testing. A seemingly abnormal result could be due to a minor, harmless fluctuation. Conversely, it could be an early indicator of an underlying heart condition requiring attention. Further investigation helps determine the true cause of the borderline result.
Common Causes of Borderline ECG Readings
Several factors can contribute to a borderline ECG reading. These factors can be broadly categorized as:
- Technical Factors:
- Improper Electrode Placement: Even slight inaccuracies in electrode placement can affect ECG readings.
- Patient Movement: Movement during the test can introduce artifacts and distort the results.
- Electrical Interference: External electrical devices can interfere with the ECG signal.
- Physiological Factors:
- Normal Variations: Heart rhythms can naturally vary from person to person. What’s considered normal for one individual may be slightly outside the typical range for another.
- Age: Age-related changes in the heart can affect ECG readings.
- Body Position: Body position during the ECG can sometimes influence the results.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Stress and Anxiety: Stress and anxiety can temporarily alter heart rhythm.
- Caffeine and Alcohol Consumption: These substances can stimulate the heart and affect ECG readings.
- Smoking: Nicotine can affect heart rate and blood pressure, potentially leading to borderline results.
- Dehydration: Dehydration can affect electrolyte balance, which can influence heart rhythm.
- Lack of Sleep: Insufficient sleep can disrupt heart rate variability.
- Underlying Medical Conditions:
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Imbalances in electrolytes like potassium, magnesium, and calcium can disrupt heart rhythm.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect heart rate and rhythm.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): High blood pressure can lead to changes in the heart that may be reflected in the ECG.
- Coronary Artery Disease: Narrowing of the coronary arteries can sometimes cause subtle changes in the ECG.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can affect heart function.
- Sleep Apnea: This condition can cause fluctuations in heart rhythm during sleep.
Understanding Your Individual Risk Factors
Interpreting a borderline ECG requires considering your individual risk factors for heart disease. These factors can influence the significance of the ECG findings and help guide further evaluation. Key risk factors include:
- Age: The risk of heart disease increases with age.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease increases your risk.
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure puts extra strain on the heart.
- High Cholesterol: High cholesterol levels can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Diabetes: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Obesity: Obesity increases the risk of several heart disease risk factors, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity increases the risk of heart disease.
Next Steps After a Borderline ECG
If you’ve received a borderline ECG result, your doctor will likely recommend further testing to gain a more comprehensive understanding of your heart health. Common follow-up tests include:
- Repeat ECG: A repeat ECG may be performed to confirm the initial findings and rule out any technical errors.
- Holter Monitor: This portable device continuously records your heart’s electrical activity for 24-48 hours or longer, providing a more detailed assessment of your heart rhythm than a standard ECG.
- Event Monitor: Similar to a Holter monitor, an event monitor records heart activity, but it’s typically worn for a longer period (up to 30 days) and is activated only when you experience symptoms.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound of the heart provides images of its structure and function, helping to identify any abnormalities in the heart valves, chambers, or blood vessels.
- Stress Test: This test monitors your heart’s activity during exercise to detect any signs of ischemia (reduced blood flow to the heart) or arrhythmias that may not be apparent at rest. Different types of stress tests exist, including treadmill stress tests, nuclear stress tests, and stress echocardiograms.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to check for electrolyte imbalances, thyroid disorders, or other underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to the borderline ECG result.
Your doctor will determine the most appropriate follow-up tests based on your individual risk factors, symptoms, and the specific findings of the borderline ECG.
Lifestyle Modifications for Heart Health
Regardless of the underlying cause of a borderline ECG, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly improve your cardiovascular health and reduce your risk of future heart problems. Key lifestyle modifications include:
- Diet:
- Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Reduce sodium intake.
- Exercise:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Include strength training exercises at least twice a week.
- Stress Management:
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Engage in hobbies and activities you enjoy.
- Seek support from friends, family, or a therapist.
- Smoking Cessation:
- Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to improve your heart health.
- Seek help from your doctor or a smoking cessation program.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption:
- If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
- Adequate Sleep:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
Open communication with your healthcare provider is essential for understanding and managing a borderline ECG result. Be sure to:
- Ask questions about the meaning of the results, potential causes, and recommended next steps.
- Provide your doctor with a complete medical history, including any symptoms you’re experiencing, medications you’re taking, and family history of heart disease.
- Discuss any concerns you have about the tests or treatment options.
- Follow your doctor’s recommendations for follow-up testing and lifestyle modifications.
The Role of Technology in ECG Interpretation
Advancements in technology, particularly artificial intelligence (AI), are playing an increasingly important role in ECG interpretation. AI algorithms can analyze ECG data and identify subtle patterns that may be missed by human readers. However, it’s important to remember that AI should be used as a tool to assist healthcare professionals, not replace them. Human oversight and clinical judgment remain crucial for accurate ECG interpretation and patient care.
Conclusion
Receiving a borderline ECG result can be unsettling, but it’s important to remember that it’s not a diagnosis. It’s a signal that further investigation is needed to determine the underlying cause and ensure your heart health. By understanding the potential causes of a borderline ECG, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can take proactive steps to protect your cardiovascular well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- A borderline ECG indicates that the test results are not definitively normal or abnormal.
- Several factors can contribute to a borderline ECG reading, including technical factors, physiological factors, lifestyle factors, and underlying medical conditions.
- Interpreting a borderline ECG requires considering your individual risk factors for heart disease.
- Follow-up testing is often recommended to gain a more comprehensive understanding of your heart health.
- Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly improve your cardiovascular health.
- Open communication with your healthcare provider is essential for understanding and managing a borderline ECG result.
- AI can assist with ECG interpretation, but human oversight remains crucial.
- Mindfulness Exercises For Anxiety PDF To Reduce Stress - February 26, 2026
- Mindfulness Activities for Adults PDF for Stress Relief - February 25, 2026
- Mindfulness Techniques PDF Offers Free Exercises for Calm and Focus - February 24, 2026